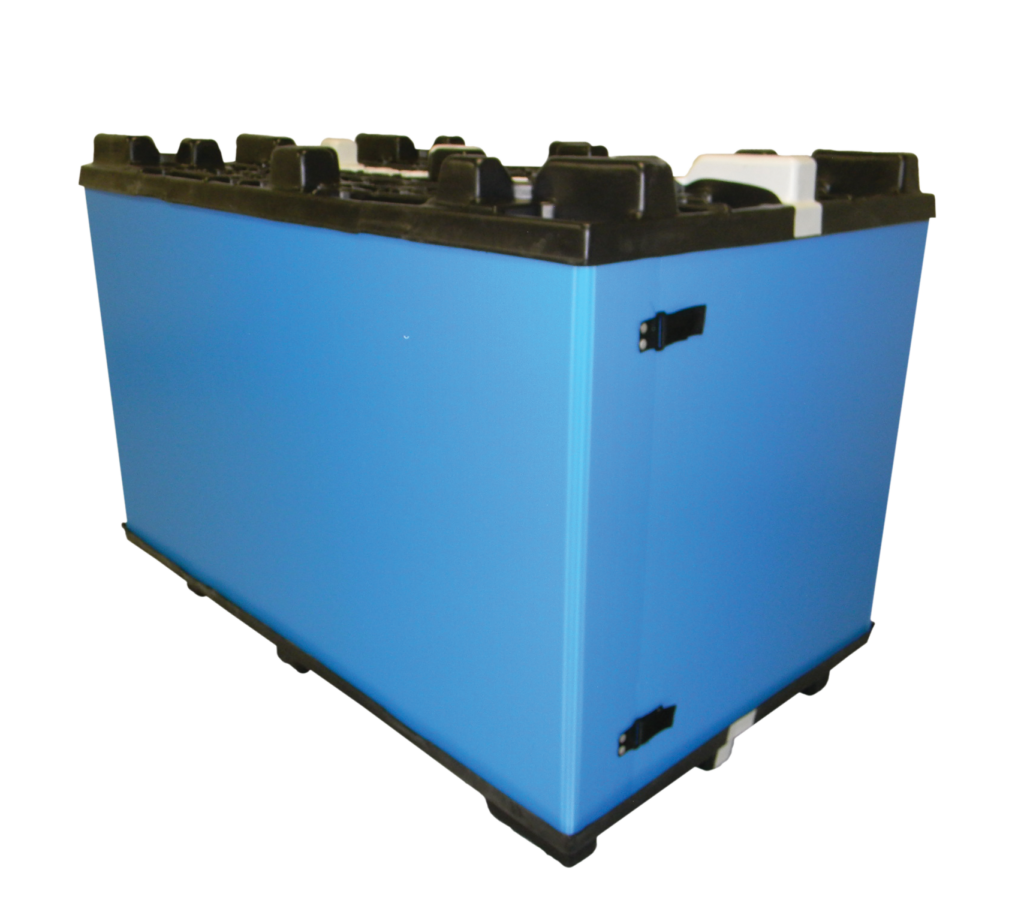
Returnable packaging containers are transforming modern supply chains by replacing traditional single-use packaging with durable, sustainable solutions. Made from high-quality materials such as corrugated plastic, foam, metal and textiles, these containers are designed for repeated use, significantly reducing waste and operational costs. Industries like automotive, electronics, medical, military, and pharmaceuticals are embracing these robust solutions to enhance product protection, streamline logistics, and meet sustainability goals.
This article explains the concept, benefits, materials, and key considerations for selecting returnable packaging solutions.
What Are Returnable Packaging Containers?
Returnable packaging containers are designed for repeated use throughout the logistics process. Unlike disposable alternatives, they form a closed-loop system where containers are returned and reused after each cycle. For example, an automotive manufacturer might use sturdy plastic bins to ship parts to an assembly plant, then have those same bins reused for subsequent shipments. This model minimizes waste and reduces cost by eliminating the need for frequent repurchasing of single-use packaging. Common types include:
- Totes and Bins: Stackable, lightweight containers for small items.
- Dunnage Assemblies: Plastic, foam or textile inserts that secure and protect products.
- Cut and Weld Containers: Custom corrugated plastic containers fabricated to precise dimensions.
- Metal Racks: Heavy-duty solutions for large or irregular items.
- Sleeve Packs: Collapsible containers designed for efficient return logistics.
These solutions are adaptable and can be customized to meet specific industry requirements, ensuring maximum product safety and streamlined operations.
Benefits of Returnable Packaging for Businesses
Adopting returnable packaging offers several advantages, making it an attractive investment for companies aiming for operational excellence.
Long-Term Cost Savings
Although the initial investment for reusable packaging may be higher, its longevity and durability result in substantial savings over time. Businesses can reduce expenditures on disposable materials and lower disposal costs, leading to improved overall packaging economics.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Reusable packaging significantly cuts down on waste. By reducing reliance on single-use materials, companies can lower their environmental footprint, conserve resources, and contribute to broader sustainability initiatives. This approach not only meets regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation among eco-conscious consumers.
Enhanced Product Protection
Engineered for durability, containers used in industrial packaging provide superior product protection. Whether through foam cushioning for delicate items or rigid containers for heavy components, these solutions minimize damage during transit. Improved protection leads to better inventory management and higher customer satisfaction.
Streamlined Logistics and Operational Efficiency
Standardized, reusable packaging simplifies handling, storage, and transportation. With uniform container designs, efficiency is improved through faster loading and unloading times, better stackability, and optimized warehouse organization. This streamlined approach leads to enhanced productivity and reduced downtime.
Materials Commonly Used in Returnable Packaging
The choice of material is crucial to the performance and suitability of returnable packaging. Each material offers unique advantages:
Corrugated Plastic
Lightweight yet durable, corrugated plastic is moisture-resistant and customizable. It is ideal for creating tailored containers that protect delicate or sensitive items, making it a popular choice in electronics and medical applications.
Foam
Foam is used for shock absorption and cushioning. Variants like polyethylene and polyurethane foam provide varying degrees of rigidity and softness, ensuring that fragile goods are protected from impacts during handling and transit.
Metal
For demanding applications, metal—often in the form of steel—is preferred for its strength and high load capacity. Metal racks and carts are well-suited for work in process and material handling.
Textiles
Textile dunnage offers a flexible, soft option that conforms to unique product shapes. Ideal for protecting scratch-sensitive items, textiles are washable and reusable, providing an extra layer of safeguarding without compromising on sustainability.
By understanding the qualities of these materials, businesses can select the best option that aligns with their operational needs and industry standards.
Making Returnable Packaging Work: Practical Implementation
While the advantages of returnable packaging are clear, successful implementation hinges on understanding the practical aspects of integrating these systems into your operations. Let’s delve into some key considerations to ensure a smooth and efficient transition.
Streamlining the Return Flow: The Closed-Loop Cycle
Returnable packaging operates on a closed-loop system, and understanding this cycle is crucial. Typically, the return process involves several key steps, often a collaborative effort between you and your packaging provider, and sometimes your customers or partners:
- Delivery and Unpacking: Your products arrive at their destination in robust returnable containers. Recipients unpack the goods, just as with traditional packaging.
- Container Collection: Once empty, containers are consolidated at the receiving location. This might involve designated collection points or scheduled pickups, depending on the scale and logistics of your operation.
- Return Transportation: Containers are then transported back to a designated point for processing. This reverse logistics leg needs to be efficiently planned to minimize costs and environmental impact. Optimized routes and consolidation strategies are key here.
- Inspection and Sorting: Upon arrival, containers are inspected for damage, wear and tear, or contamination. They are then sorted based on type, condition, and cleaning requirements.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: A critical step is the thorough cleaning and maintenance of containers. This ensures hygiene, prolongs container lifespan, and maintains performance. Cleaning methods vary depending on the material and industry needs, ranging from simple washing to more specialized sanitization processes.
- Repackaging and Reuse: Cleaned and inspected containers are then made ready for their next cycle, ensuring they are available for outbound shipments. This completes the loop, ready to deliver value again and again.
Smart Tracking for Efficient Management
To manage a returnable packaging system effectively, robust tracking is essential. Imagine knowing exactly where your containers are at any point in time! This is achievable through various tracking technologies:
- Barcodes: A cost-effective and widely used solution, barcodes allow for basic scanning and tracking at key points in the supply chain.
- RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) Tags: Offering more advanced tracking capabilities, RFID tags can be read wirelessly, even in bulk, speeding up inventory management and providing real-time visibility.
- QR Codes: Similar to barcodes but capable of holding more information, QR codes can be easily scanned with smartphones, potentially involving partners or even end-users in the tracking process (where applicable).
Choosing the right tracking system depends on your budget, the complexity of your supply chain, and the level of detail you require. Effective tracking not only minimizes container loss but also optimizes inventory levels, ensuring you have the right containers available when you need them.
Maintaining Cleanliness and Longevity
The repeated use of returnable containers necessitates proper cleaning and maintenance to guarantee hygiene, product integrity, and container lifespan. Cleaning procedures should be tailored to the materials used and the specific industry requirements. For example:
- General Industrial Use: Simple washing with soap and water or industrial detergents may suffice for many applications.
- Food and Beverage: More rigorous sanitization processes are essential, potentially including high-pressure washing, steam cleaning, or chemical sanitization to meet strict hygiene standards.
- Pharmaceutical and Medical: Sterilization protocols might be required, demanding specialized cleaning agents and processes to ensure containers meet stringent regulatory requirements.
Regular inspection for damage and wear is also crucial. Prompt repairs or replacement of damaged components will prevent minor issues from escalating and extend the overall life of your container fleet.
Navigating Reverse Logistics and Costs
While returnable packaging offers long-term cost savings, understanding and managing reverse logistics costs is important. These costs primarily stem from:
- Transportation of Empty Containers: The fuel and labor associated with returning empty containers. Optimizing routes, consolidating shipments, and working with efficient logistics partners can significantly reduce these expenses.
- Cleaning and Maintenance Operations: The cost of cleaning agents, labor for cleaning and inspection, and repair materials. Establishing efficient cleaning processes and preventative maintenance schedules helps control these costs.
- Tracking System Implementation and Management: The initial investment in tracking technology and the ongoing operational costs of managing the tracking system. Choosing a system that aligns with your needs and offers scalability is key to maximizing ROI.
However, it’s crucial to remember that these reverse logistics costs are often offset by the elimination of costs associated with purchasing and disposing of single-use packaging, as well as reduced product damage and improved operational efficiency. A comprehensive cost analysis, considering both forward and reverse logistics, will reveal the true economic advantages of returnable packaging.
Planning for Space: Accommodating the Return Flow
Integrating returnable packaging does require some space planning adjustments. You’ll need to consider space for:
- Incoming Empty Containers: Designated areas to receive and temporarily store empty containers awaiting processing.
- Cleaning and Maintenance Zones: Space for cleaning equipment and maintenance activities.
- Storage of Clean, Ready-to-Use Containers: Organized storage for containers ready for outbound shipments.
However, with smart planning, these space requirements can be efficiently managed. Collapsible container designs, vertical stacking systems, and optimized warehouse layouts can help minimize the footprint needed for your returnable packaging system.
By carefully considering these practical implementation details, businesses can confidently embrace returnable packaging and unlock its full potential for cost savings, sustainability, and operational excellence.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Returnable Packaging Containers
Choosing the right container involves evaluating several critical factors:
Durability and Longevity
Since these containers are intended for multiple uses, they must withstand impacts, environmental changes, and repeated handling. Opt for materials tested for durability in your specific operational conditions.
Customization
Different industries have unique packaging needs. Evaluate whether your products require custom dimensions, foam inserts, or specialized finishes to ensure optimal protection and functionality.
Operational Efficiency
Packaging should facilitate easy stacking, nesting, and transport. The design must align with your logistical workflows to minimize handling time and maximize storage space.
Transport Compatibility
Consider challenges with packaging for transportation and local distribution such as shock, impact, vibration, weather exposure, theft and tampering, and space optimization. Containers should have features such as secure closures and impact resistance to protect products over various transit conditions.
Regulatory Compliance
For sectors like medical and pharmaceutical, adherence to strict safety and sterility standards is critical. Ensure your packaging solutions meet all relevant guidelines and certifications.
Cost and Return on Investment
Conduct an ROI analysis to understand the long-term savings versus the initial expenditure. Reusable packaging generally offers better economics over time through reduced material costs and lower waste disposal fees.
Environmental Impact
Evaluate the recyclability and overall ecological footprint of the packaging material. Choose options that contribute to your sustainability goals and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Customization and Tailored Solutions for Your Packaging Needs
Every business has unique logistical challenges, making customization a vital component of effective packaging strategies. Tailored solutions can address specific requirements such as size, shape, cushioning, and compliance needs. Whether integrating foam inserts for enhanced shock absorption or designing collapsible containers for more efficient return logistics, a customized approach offers increased product safety and operational efficiency. Tailoring packaging also leads to better space utilization and reduced waste, further supporting sustainability efforts.
Many organizations provide specialized services for returnable packaging. By working closely with clients, suppliers can design packaging systems that address specific industry challenges while optimizing supply chain processes.
Returnable Packaging and Sustainability Goals
Sustainability is a driving factor behind the shift to returnable packaging. According to the EPA’s Guidelines on Reducing Waste in Packaging, reusable containers drastically reduce waste by eliminating the need for single-use materials. Their extended lifespan means fewer replacements, lowering the environmental impact associated with production, transportation, and disposal. Adopting these solutions not only supports eco-friendly initiatives but also positions companies as responsible and forward-thinking.
By reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving resources, returnable packaging helps organizations meet both internal sustainability targets and external regulatory requirements.
Universal Package’s Offerings and Services
Universal Package offers a comprehensive range of Industrial Packaging and Material Handling Solutions. Businesses can choose from Reusable Packaging Solutions that include corrugated plastic boxes, cut and weld containers, foam assemblies, textile dunnage, and steel racks. Complementary services—like Cleaning and Repair Services and Lease and Rental Options—support the entire lifecycle of returnable packaging investments.
Whether you are shipping high-value electronics, transporting automotive parts, or simply requiring top-tier Packaging for Storage, Universal Package aims to provide a tailored system that optimizes both protection and logistics.
For additional guidance or a quote for specific reusable packaging, Contact Universal Package.
Transitioning to a Reusable Packaging Future
Returnable packaging containers offer a transformative solution for modern supply chain challenges, delivering cost efficiency, robust product protection, and significant sustainability benefits. By carefully selecting appropriate materials, considering key operational factors, and leveraging customized solutions, businesses can achieve substantial long-term savings and environmental advantages. These containers also streamline packaging for transportation and ensure proper packaging for storage, ultimately boosting operational effectiveness.
Embrace the future of logistics by switching to reusable packaging—enhance your supply chain, reduce waste, and support a sustainable future. To learn how you can customize a returnable packaging system for your specific industry needs, consult the experts at Universal Package’s Packaging Solutions and discover how tailored approaches can elevate your business success.